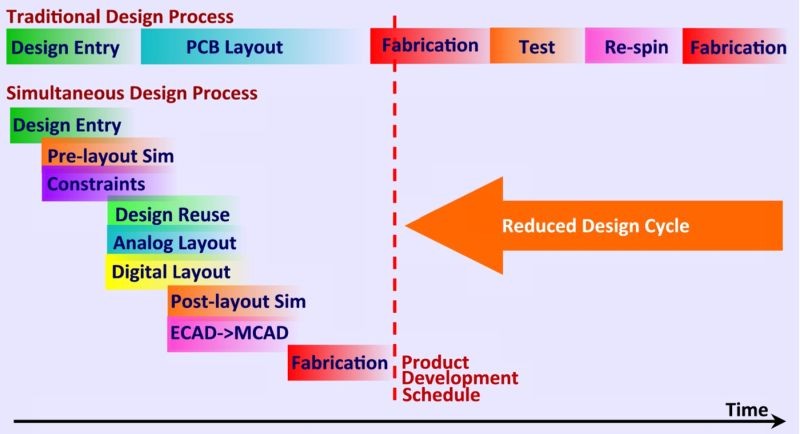
Pre-Layout Simulation Validates Circuit Design
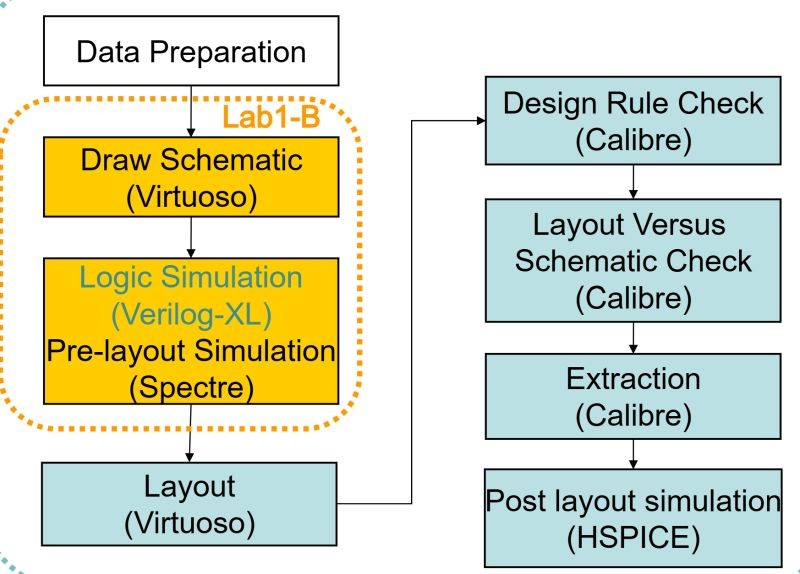
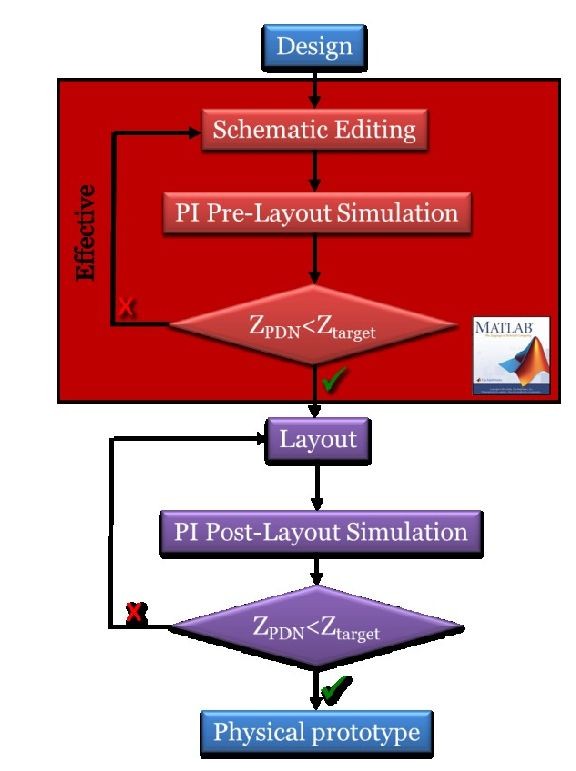
To ensure the circuit design aligns with the specifications, simulations are conducted in two main stages: pre-layout and post-layout. In this post, we will explore the significance of pre-layout simulations.
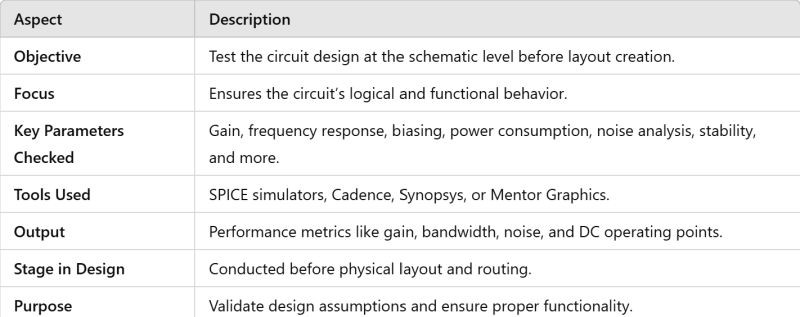
Before creating the layout, pre-layout simulation verifies the circuit’s logical and functional behavior at the schematic level.
The key parameters checked during pre-layout simulation include:
DC_Operating_Point (Biasing):
Ensures that the circuit operates at the correct DC operating points, such as bias voltages and currents for transistors or other active devices.
Verifies the correct startup conditions of circuits like amplifiers, voltage references, etc.
Gain_and_Frequency_Response:
Voltage Gain: Checks the amplification characteristics of the circuit.
Frequency Response: Verifies the frequency bandwidth of the circuit (e.g., low-pass, high-pass, band-pass behavior).
Transient Response: Simulates how the circuit reacts to input signals over time, especially for circuits that need to work in time-sensitive applications.
Power_Consumption:
Power Dissipation: Ensures that the circuit doesn’t consume more power than the design specification allows.
Current Consumption: Measures the current drawn from the power supply, especially critical in battery-powered devices.
Input and Output Impedance
Verifies the impedance of the input and output ports to ensure compatibility with the source and load and to avoid signal reflection or excessive power loss.
Noise_Analysis:
Thermal Noise: Simulates the thermal noise generated by resistive elements in the circuit.
Flicker Noise: Checks the low-frequency noise, especially for MOSFETs, which might impact the performance of low-noise amplifiers or precision analog circuits.
Total Integrated Noise (TIN): Evaluates the total noise performance of the system.
Stability_and_PhaseMargin:
Phase Margin: Ensures that the system is stable and won’t oscillate or become unstable when operating with feedback.
Loop Gain: Verifies that the feedback loop gain is within acceptable limits.
AC_Small-Signal_Analysis:
Ensures the small-signal behavior of the circuit meets the design requirements. This includes calculations for bandwidth, slew rate, and slew rate limitations.
Linearity_and_Distortion:
Verifies that the circuit operates linearly in the desired input range and that distortion (harmonic, intermodulation) remains within acceptable limits.
Temperature_and_ProcessVariation:
Simulates the circuit’s response under different temperature conditions and process variations (e.g., manufacturing variations), ensuring robustness across environmental changes.